Avoiding Copyright Issues on Amazon in 2025
Copyright infringement has become a growing concern across Amazon, with both valid and false claims increasing every year. If you sell on Amazon, you already know how disruptive these issues can be for your business. This guide breaks down everything sellers need to understand about Amazon copyright infringement and how to manage it effectively.
Amazon Copyright Infringement – Introduction
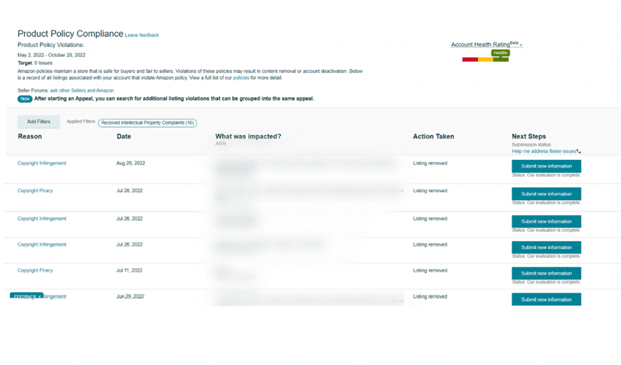
Dealing with copyright or trademark infringement on Amazon can be stressful and damaging, no matter how the dispute ends. Amazon strictly enforces intellectual property (IP) protection, which includes removing or restricting listings that violate IP rights. One of Amazon’s key tools for brand owners is the Brand Registry, which allows approved brands to report unauthorized sellers, counterfeit listings, and misuse of brand content.
By registering your brand within Amazon Brand Registry, you can protect your IP—whether it’s a trademark, patent, or copyrighted materials. Once registered, Amazon can automatically take down any listing elements that violate your rights.
Complying with Amazon’s Selling Guidelines
When selling on Amazon, you must follow all federal, state, and local laws, along with Amazon’s seller policies. You’re also prohibited from infringing on the intellectual property of other brands. If you want to use images in your product listings, you must either own the copyright or have permission to use them. Otherwise, you may face legal consequences or even the loss of your selling privileges.
Reporting Copyright Infringement on Amazon
Copyright infringement can occur in several ways, and Amazon allows you to report violations at multiple levels:
- ASIN-Level: If you find your images or written content used on a product, packaging, or listing without your consent, you can file a copyright claim against the ASIN.
- Image or Text-Level: If your photos or text appear in a listing without permission, you can report the content even though the product page will remain live.
- Seller-Level: If a specific seller’s offer violates your copyright, you can report that seller. The ASIN stays live, but the seller’s offer may be removed.
You can also report situations where someone uses your brand without approval, hijacks your ASIN, or profits from your intellectual property illegally.
Keep in mind that uploading images to Amazon gives them a non-exclusive right to use those images for marketing and listing purposes. This also means other sellers might list under the same ASIN. Because of this, asserting copyright claims later can sometimes be more challenging.
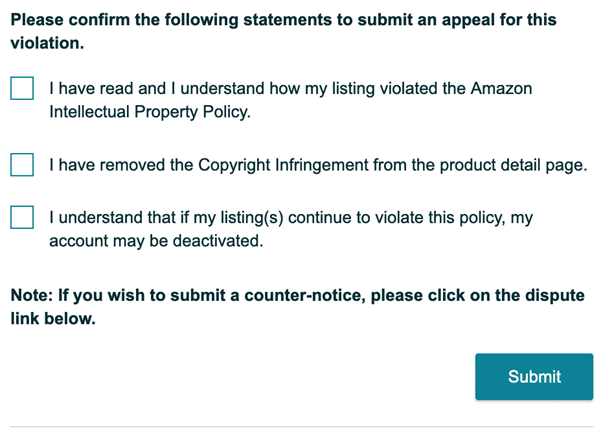
How to File a Copyright or Trademark Infringement Claim on Amazon
If you believe your brand or product is affected by copyright or trademark misuse, Amazon requires that you submit your complaint through its designated IP report forms.
Brand Registry users have access to the Report a Violation (RAV) dashboard, which can also be used to file patent and other IP-related complaints.
When submitting a claim, you must provide:
- A physical or electronic signature confirming your ownership
- A description of the copyrighted, trademarked, or patented work involved
- Information about the infringing material (product, packaging, text, or images)
- ASINs or product detail page URLs, and whether the complaint targets all or specific sellers
- Your contact details (address, phone number, email)
- Additional information, such as order IDs from test buys
- A “good-faith belief” statement asserting the unauthorized use
- A declaration under penalty of perjury confirming accuracy and ownership
- A notice sent to Amazon’s copyright agent via the official form or email (copyright@amazon.com)
Important Notes About Product Listings and IP Enforcement
Product detail pages remain permanent once created, even when your inventory runs out. When you upload copyrighted images or details, you grant Amazon and its partners the right to use them to support the listing. While Amazon instructs sellers to match listings accurately, some sellers may still misuse your content or list mismatched products under your ASIN.
If this happens, you can still report the issue using Amazon’s infringement forms. However, Amazon may only enforce IP claims within the marketplace where the IP is officially registered. For example, a U.S. trademark may not be enough to remove an ASIN from Amazon Canada.
MAP Violations – What Sellers Should Know
Manufacturers may enforce MAP (Minimum Advertised Price) or exclusive distribution agreements. However, Amazon does not enforce MAP policies, as these disputes fall strictly between the brand owner and the seller. Amazon’s involvement is limited to cases involving intellectual property violations—not pricing disagreements.


